FarSync FAQ – Linux
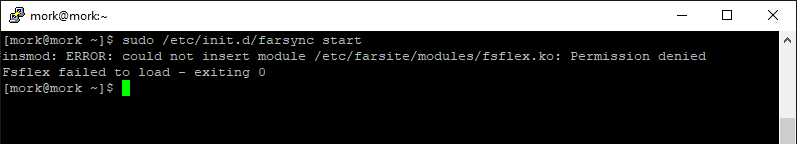
If this error occurs when insmod is trying to insert a module, such as in the error case shown below, then this is normally due to SELinux:
To check the status of SELinux, run:
$ sestatus
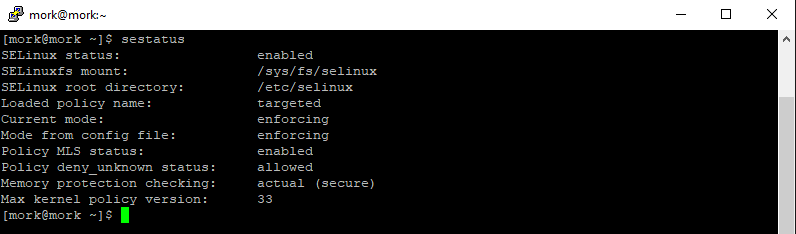
In this case, SELinux’s status is showing as being set to enabled and its current mode set to enforcing.
We can change the SELinux configuration, to stop it preventing the driver from loading, by setting SELinux’s current mode to permissive:
sudo setenforce permissive

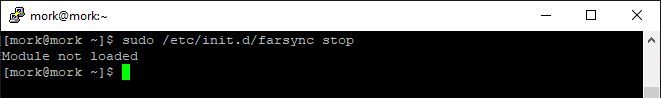
We can then confirm the effect, of making that change, by firstly making sure that farsync is stopped, using:
sudo /etc/init.d/farsync stop
and then starting farsync again, using:
sudo /etc/init.d/farsync start
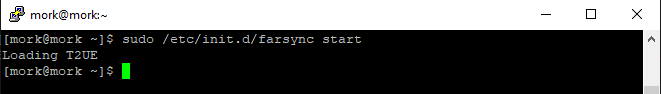
Note that in this case the “Permission denied” error is no longer displayed.
Note that this effect will persist whilst subsequently stopping and starting farsync (until the next time the system is restarted):
In the above example, it definitely indicates that the original condition was caused by SELinux issue. At this point, we can either:
- Leave SELinux in permissive mode, in which case we need to make sure the permissive setting is carried across reboots by editing the /etc/selinux/config file and setting SELINUX=permissive.

- Set SELinux’s mode back to enforcing and add a custom policy module, which can either be done manually or via a script. An example script is available here which demonstrates creating a custom policy module and loading the newly created policy module.
The document below specifies how to get LAPB up and working with FarSync Adapters on Linux. It illustrates this using RedHat Enterprise Linux 8, but the same process applies to other distributions.
The serial number of your adaptor can be found on a label affixed to the adaptor
For a Flex the serial number label is attached to the side of the Flex:

For a PCIe/PCI card the serial number label is attached to the P.C.B:

Alternatively, once logged in to the Linux platform, start a terminal session if not already done so. Then enter cat /proc/fsflex to display the details of any Flex adaptors and cat /proc/farsync to display the details of FarSync cards. The serial number for each card is reported among the information returned. In the examples below, the card serial number is in red:
mesh2@mesh2:~> cat /proc/fsflex
FarSync OEM Driver version 4.0.0 – Patch Level 00 – Build -b401
1 Cards found
sync6-sync6:(U2050111) FarSync Flex-1 (v2) IRQ0, 1 ports, State: Running
Total number of ports = 1
mesh2@mesh2:~>
mesh2@mesh2:~> cat /proc/farsync
FarSync OEM Driver version 4.0.0 – Patch Level 00 – Build -b401
2 Cards found
sync0-sync1:(M3210002) FarSync T2Ee IRQ30, 2 ports, State: Running
sync2-sync5:(K6427019) FarSync T4Ue IRQ32, 4 ports, State: Running
Total number of ports = 6
mesh2@mesh2:~>
There could be an IRQ routing issue, try disabling the APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller), by booting the system using the noapic kernel parameter.
The method for disabling the APIC will depend on the Linux distribution and boot loader, below is an example for openSUSE 15.4:
Open /etc/default/grub for editing
mindy@localhost:~> sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Go to the line that starts GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT =
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=”splash=silent preempt=full mitigations=auto quiet security=apparmor”
Add noapic to the end of the line
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=”splash=silent preempt=full mitigations=auto quiet security=apparmor noapic”
Save the file
Update the bootloader
mindy@localhost:~> sudo update-bootloader −−refresh
mindy@localhost:~>
Reboot the system
Once rebooted you can confirm that the system has booted using the noapic option, by using cat /proc/cmdline, which displays the boot command line:
mindy@localhost:~> cat /proc/cmdline
BOOT_IMAGE=/boot/vmlinuz-5.14.21-150400.24.55-default root=UUID=8f07be5e-604e-4270-b079-8456cf1ad694 splash=silent preempt=full mitigations=auto quiet security=apparmor noapic
mindy@localhost:~>
If this error occurs when insmod is trying to insert a module, such as in the error case shown below, then this normally indicates that the driver has been built for a different version of the kernel compared with the one that is currently running:
insmod: ERROR: could not insert module /etc/farsite/modules/farsync.ko: Invalid module form
Ensure that the /usr/src/linux link that you created at install time, still matches the current kernel version as reported by: uname -r
e.g.
build@ubuntu:~/farsync-5.0.3-b004$ uname -r
5.15.0-84-generic
build@ubuntu:~/farsync-5.0.3-b004$
build@ubuntu:~/farsync-5.0.3-b004$ ls -l /usr/src
total 36
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 40 Sep 28 11:22 linux -> /usr/src/linux-headers-5.15.0-84-generic
drwxr-xr-x 7 root root 4096 Sep 18 11:14 linux-headers-5.15.0-83-generic
drwxr-xr-x 7 root root 4096 Sep 26 09:44 linux-headers-5.15.0-84-generic
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Feb 9 06:46 linux-hwe-5.11-headers-5.11.0-41
drwxr-xr-x 24 root root 4096 Feb 8 06:55 linux-hwe-5.13-headers-5.13.0-28
drwxr-xr-x 24 root root 4096 Feb 24 04:42 linux-hwe-5.13-headers-5.13.0-30
build@ubuntu:~/farsync-5.0.3-b004$
If the link doesn’t exist, or points to headers for a different kernel version, you should then (re)create the link and reinstall the driver (or run the update script) – see the installation documentation for more details on setting up the link and the corresponding (re)installation sequence.
